SG Castings Ltd
Walverden Foundry / Brook St
Nelson
Lancashire BB9 9PU
TEL: 01282 615238
SG Castings Ltd
Walverden Foundry / Brook St
Nelson
Lancashire BB9 9PU
TEL: 01282 615238
SG Iron, also known as spheroidal graphite, nodular or ductile iron was invented in 1943 when a magnesium treatment was discovered to form a ferrous alloy for ductile iron.
Ductile cast iron is supplied in accordance with BS2789 or BSEN1563 designations.
When compared with grey iron, ductile iron has a higher impact resistance combined with greater tensile strength, elongation and ductility. These characteristics together make for a finished product with very good wear resistance qualities.
Ductile Iron is not a single material, but a general term for a range of grades of metals that share certain common defining factors, in this case the shape of the graphite elements of the finished product.
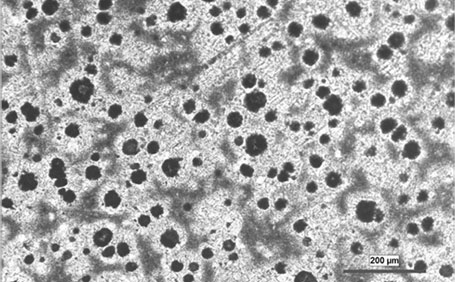
Cast iron includes graphite. In grey iron this graphite is in the form of flakes, but in ductile iron the graphite particles are nodular. This composition means that the metal has a very low propensity to crack - the nodules actively inhibit the process of cracking meaning the material has much more ductility - hence the common name of ductile iron. In layman terms, ductility simply means stretchiness - the ability of a material to be deformed and then return to its original shape.
The nodules are created because of the addition of magnesium to the iron - magnesium melts at around 200 degrees less than iron and this has a nodulizing effect on the graphites. Magnesuim works because it forms carbides which when added to melting iron form carbon islands around the graphite elements - holding them in a nodular shape.
At SG Castings we mostly cast in grade 450/10 ductile cast iron but have the facilities to cast in a range of SG and grey iron grades.
Ductile iron is a suitable material for a wide range of industries.
Where strength requirements need to surpass that of aluminium and grey iron, but where steel is not suitable, ductile iron finds a niche.
Ductile iron is used for components where a high resistance to wearing, or a high level of ductility is needed.